Some of the most treasured early-age artwork comes from a period even before the Renaissance Era had begun, a period that went on during the early Middle Ages – it is the period of the Gothic Artwork.
Gothic artwork such as architecture, sculpture, paintings, stained glass and even illuminated manuscripts were produced in Europe towards the end of the middle Ages. This kind of artwork was first produced in France in the year 1140 and spread to all the other European countries during the following centuries. The advent of the Renaissance Era in the 15th century signaled the end of the Gothic age, although this form of art was used throughout Europe even during the 16th century.
A Brief History and Introduction
- Initially, the word ‘Gothic’ was used by the Italian Renaissance writers as a sort of derogatory term for the art and architecture that came out of the middle ages, which they looked upon as the works of barbarian Goths. However, this age is now considered to be one of the finest artistic eras in Europe today.
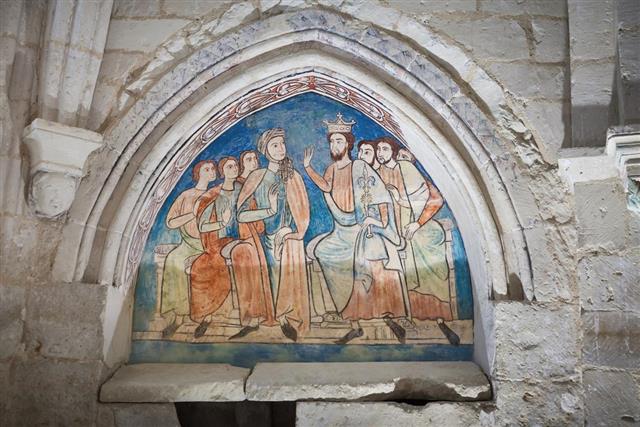
- During this period, the artwork that was most commonly seen was the paintings and sculptures that would tell narrative stories through pictures, and most of these art pieces were secular or Christian in nature.
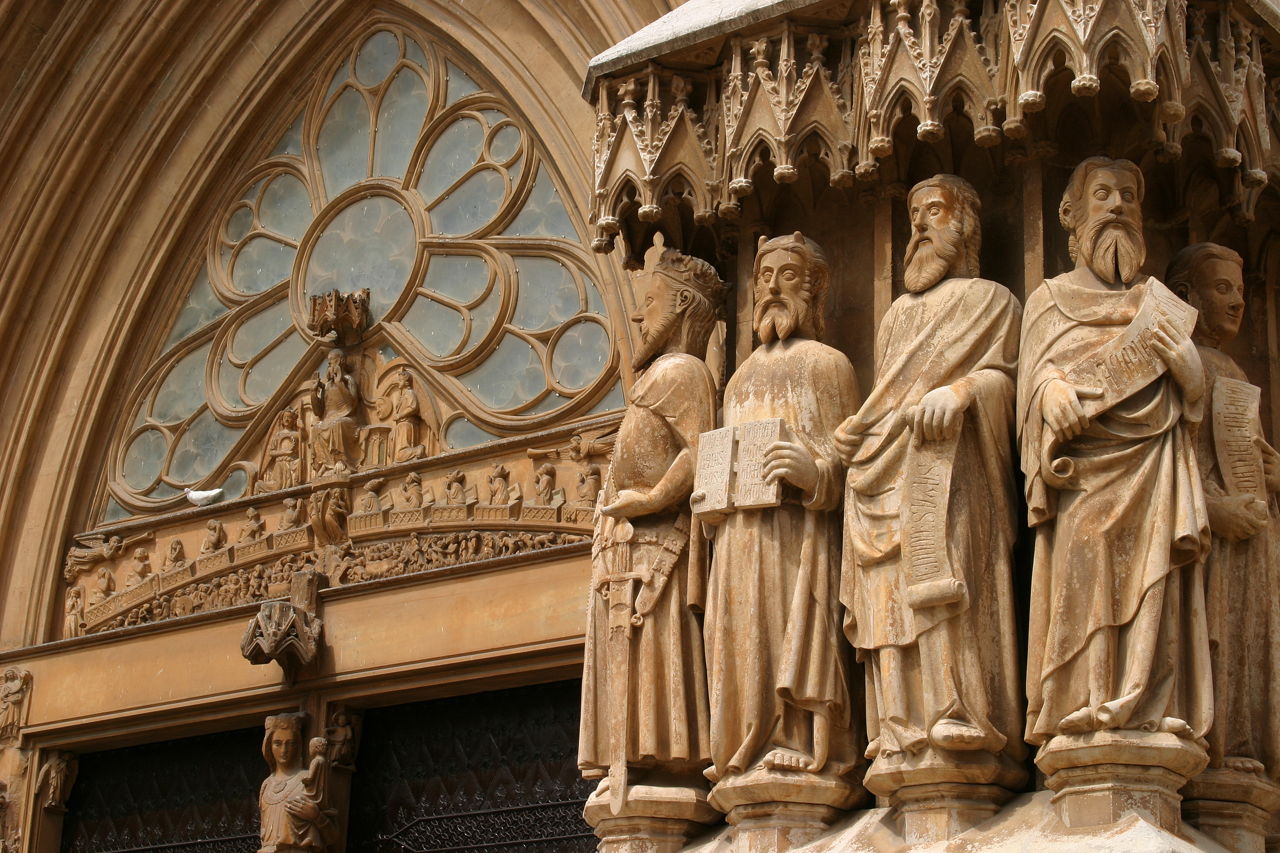
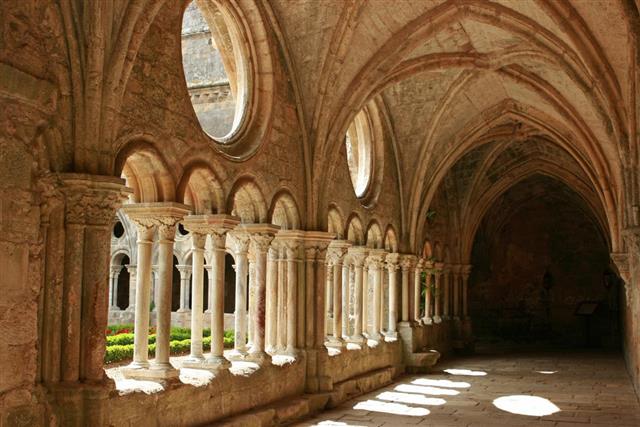
- Some of the earliest pieces of Gothic art are the sculptures found on abbey walls and in cathedrals. The first real example of Gothic artwork was the architectural works, and this type of art even became the subject matter for many stained glass windows in those days.
- The typical Gothic style paintings that further define this type of artwork wasn’t really produced until almost fifty years after Gothic sculptures and architecture came out.
- Although the break between the artwork and the Romanesque styles has still remained imprecise, the beginning of the artwork has apparently occurred in certain areas at different yet related intervals of time.
- This artwork began in France and England in the 13th century, and became popular in other places like Italy and Germany somewhere between 1220 and 1300 AD. Just like the Gothic architecture visible on church walls, Gothic paintings were also extremely narrative in nature.
- Although the paintings had a fairly short time of popularity as the preferred medium amongst budding artists during that time, there is still evidence that this type of artwork falls into four different styles, which were said to be the most common styles of paintings during that time period.
- The four styles or depictions are: the fresco, the illuminated manuscript, the panel painting, and the paintings on glass work. Of these four styles, stained glass work has still remained as a strong reminder of the glory of the Gothic art in those ages long gone, and is still being created by master artisans who have the skills and knowledge till today.
- In the case of the other three styles of paintings, frescoes went on to be used as pictorial narratives in churches and on church walls in Southern European countries, and are considered to be an incorporation of Romanesque as well as Christian traditions.
- In 13th century Italy, panel paintings became immensely popular and spread like wildfire throughout Europe. With such an incredible rise in its popularity, panel paintings became the dominant mode of artwork in the 15th century, fast becoming more popular than stained glass paintings.
- Since most of the monumental works have not survived the ages, illuminated manuscripts are still considered to be the most complete record of artwork, and has lasted the ages over most other styles of painting that have long since perished.
- As the Dark Ages moved on and the state of world began to change on the whole, so did the various interpretations of the artwork as a reflection of the changing time and attitudes. This movement became more popular and was known as the International Gothic movement in the latter half of the 15th century.
- From there on, it evolved into another type of art form that depicted not only Christian and secular allegories, but also resulted in the development of more illuminated paintings and manuscripts.
- This came about due to the rising populations in cities and universities and mainly because of the large increase in demand and trade. With such large-scale growth in the cities, more and more people were becoming aware of the value of artwork and better records were thus kept.
- The International Goth art was further developed in Bohemia, Burgundy and in Northern Italy in the late 13th century and the early 14th century. During this period, artists traveled extensively and created demand amongst the aristocracy of the time, thus banning any common concepts of the various Gothic styles.
- The main influences on this type of artwork were derived from the Netherlands, Italy and Northern France. It was during this time that features like rich coloring and flowing lines were included.
- Gothic angel art was also very popular during those dark ages. From natural, cherubic angels taking the shape of guardian angels to the darker angel art that would feature robust Renaissance era angels with halos of gold and outstretched wings, these angels were portrayed in spectacular sketches.
- The sculpture on the other hand evolved from the Romanesque style and became more naturalistic in expression towards the early 12th century and the late 13th century. Influences from Roman and Greek statuary were incorporated into facial expression, noses and even drapery.
- The famous sculptor Claus Sluter along with the changing tastes in the world of art was the first indication that the Gothic period of art had ended, and this signaled the beginning of the Renaissance era at the end of the 15th century.
- In a time where a lot of change was taking place for the common-day people, Gothic art took a back seat and fell under the broader category of medieval art that also included other such disparate styles and elements like the Celtic and Viking art.
In fact, most of the middle age artwork has a vast history of these elements that converge and conjoin into the outstanding artistic legacy that we can only read about today. The Gothic artwork has indeed contributed over the centuries to the outcome of many of the other forms of art, right from the Renaissance period to present day.